SOLUTION
Medical/Food/Daily Necessities
75% reduction in rework during packaging and packing of artificial joint
Case study at a manufacturer of orthopedic implants
| In a medical device manufacturing plant, great care is taken to prevent foreign substances from adhering to the product. This is because if foreign substances are attached to products, customers will complain and quality will become a problem. This case study describes improvements made at a manufacturing site for artificial bones, which are orthopedic implants. At this plant, artificial bones are visually inspected for foreign matter adherence when they are packaged. If foreign matter was found, the product was returned to the clean bench, dust was removed, and the product was re-packaged. Not only was it difficult to remove the adhered foreign matter even after reworking, but another foreign matter would be newly adhered during processing, creating a vicious cycle that consumed an enormous amount of time and labor to deal with. |
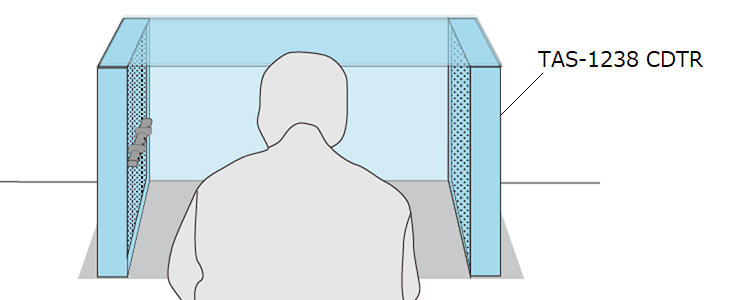 |
As a countermeasure, they introduced TRINC’s CLEAN DESKTOP TRINC (CDT) and changed the process so that packing is done after dust removal in the CDT. This enables both high foreign matter removal capability and prevention of re-adhesion. These two effects have resulted in a 75% improvement in the straightening rate compared to before the countermeasure, dramatically reducing the man-hours required for rework.